

Slide 1 - copy - copy - copy
technology-center18
types-of-soil-section-3
Perlite applications and uses
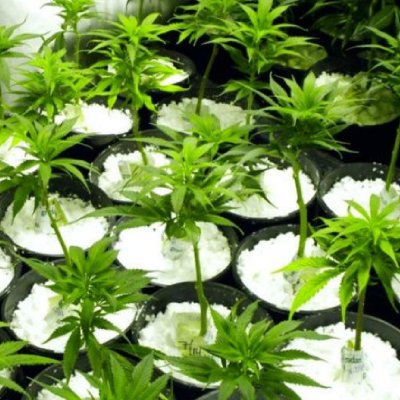

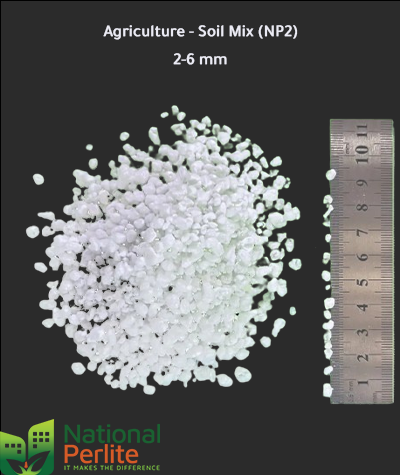
Perlite is one of nature’s best ways to grow plants. It is widely used as a soil improver due to its agricultural characteristics such as water absorption, aeration, and insulation.

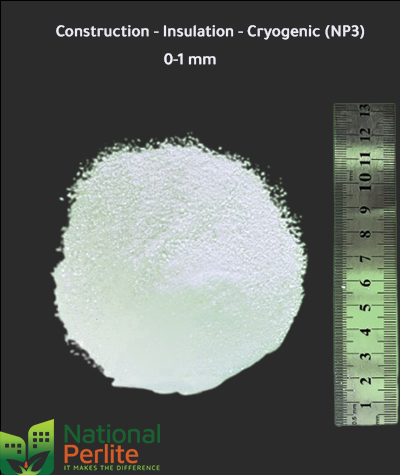
Over 50% of expanded perlite worldwide is used in the construction industry. It became an essential part of the industry due to its remarkable qualities.
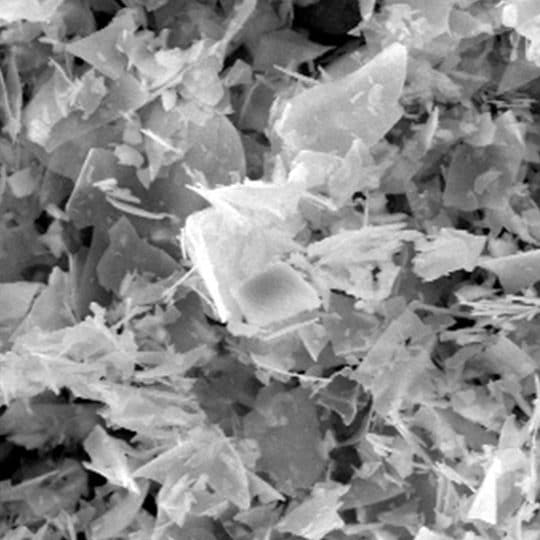
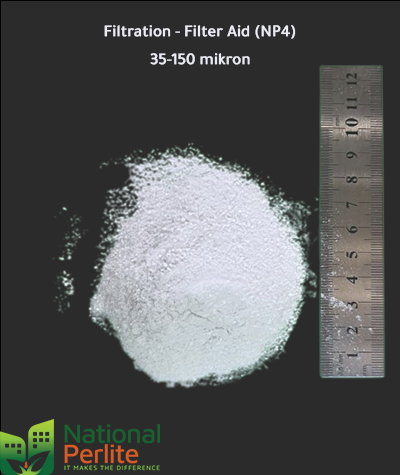
Perlite filter aids have gained acceptance in almost every industry concerned with the separation of liquids and solids, even gasses and solids

When perlite ore is heated, it grows up to 20 times its original size and forms clusters of microscopic glass bubbles that are ideal for industrial uses.
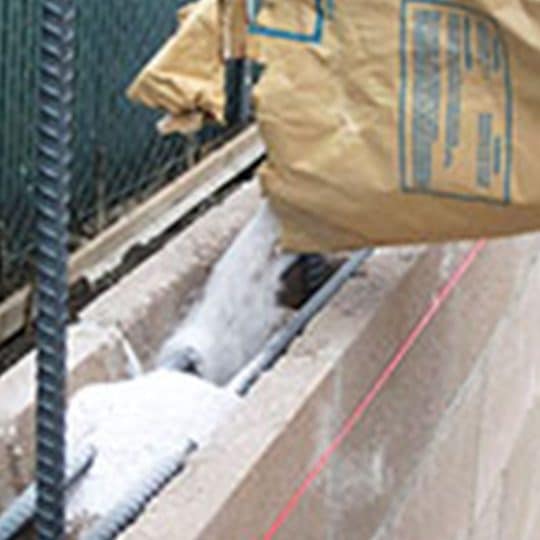

Thermal tests show significant energy savings and drastically reduced heat transmission when perlite is used to fill cavities in concrete masonry structures.
Our Products
Expanded Perlite
About Us
We are a leading manufacturer of high-quality perlite products, serving the construction, insulation, cryogenics, paints, plaster, foundry, coatings, and wide range of industries globally. Revolutionizing industries with our unmatched perlite quality. At National Perlite, we stand as the global cornerstone, committed to provide innovative and sustainable solutions, propelling industries and their innovations forward:
-
Enabling exceptional product lines for lightweight concrete manufacturers, ready-mix, and precast pioneers. our perlite, the secret to innovate with lighter, thermally superior products.
-
Insulation and cryogenic realms discover unrivaled thermal efficiency, providing vital low-temperature insulation, an edge in energy-saving solutions.
-
Offering plasters and paints manufacturers the top-line fire resistance products that sets new industry standards.
-
Transforming agriculture & horticulture with organic, cost-cutting solutions that optimizes growth, revolutionizing water use and root health.
- As a leading filter aid, our perlite brings clarity and precision to a variety of filtration processes.
-
In the world of glass and ceramics, textile we guide manufacturers to refine and perfect their craft with our premium perlite.
- National Perlite isn't just a product; it's a promise of quality, innovation, and a sustainable future.
Perlite
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE AR-SA /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt; mso-para-margin-top:0in; mso-para-margin-right:0in; mso-para-margin-bottom:8.0pt; mso-para-margin-left:0in; line-height:107%; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri",sans-serif; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-bidi-font-family:Arial; mso-bidi-theme-font:minor-bidi;} Perlite's exceptional thermal insulation properties make it indispensable in the construction and insulation
sectors, providing energy-efficient solutions and enhancing building safety.
Valued for its:
- Superior Insulation:
Offers outstanding thermal insulation in construction, from residential
insulation to high-temperature industrial applications.
- Ceramics and Glass:
In the ceramics and glass industries, perlite lightens products while
providing insulation, shaping innovations in manufacturing.
- Paints and Coatings:
Perlite is also a key ingredient in the formulation of paints and
coatings, offering matting effects, texture, and insulation within a
single application.
- Construction Versatility: Employed in a range of construction materials,
including plasters, lightweight structural elements, and as an additive in
gypsum and construction chemicals.
- Refractories:
Integral to the creation of refractory bricks and mortars, perlite
withstands and insulates against extreme temperatures.
- Agriculture and Horticulture: Beyond industrial applications, perlite promotes
plant growth through soil aeration and moisture retention, contributing to
sustainable agriculture practices.
- Asphalt Enhancement: Perlite
is incorporated into asphalt mixtures to improve durability and reduce
noise on roadways, as well as to increase thermal insulation properties,
contributing to more sustainable and longer-lasting pavement solutions.
- Chemical Resilience:
Exhibits remarkable resistance to acids, bases, and solvents, making it a
preferred choice in the production of chemical-resistant materials, like
sewer pipes.
- Water-Resistant Insulation: Utilized for waterproofing in roofing and terraces,
perlite contributes to robust building envelopes.
- Frost Resistance:
Its durability against frost makes it ideal for outdoor construction
projects, ensuring longevity and structural integrity.
- Railway Maintenance:
Perlite's lightweight and abrasive qualities aid in rail bed maintenance
for safer and smoother rail operations.
- Casting Applications:
In foundries, perlite serves as a flux and a component of foundry sands,
improving metal casting processes.
- Iron and Steel Production: Facilitates temperature control and slag management in metal production, enhancing the quality of the final products.
With perlite, industries embrace a path of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability.
What We Provide
100 Liter bags
100 L/bags of Agriculture - Construction and Insulation - Cryogenic Perlite
1000 L
1000L/bag multi use Perlite
10 Liter
10 L /bag of Agricultural Perlite
20 Kg
20kg/bags Filter Aid Perlite
Grow bags
110 cm X 20 cm X 10 cm .. GrowBag fully of perlite with 30 liter of perlite ..
Ore Perlite
0.06-1.2 mm and 1.2-2.8 mm of Ore perlite 1 sm :1250 kg
Our Team

CEO
Ali Alshamsi






